DNS or Domain Name System is the index off of the public internet. Allows you and computers to lookup computer addresses with human names. But also does much more than that.
- Authorizes email as legit
- Lets systems and people know what services are available
- Sets up system redundancy for fail-over and fail back
- Provides an authentication mechanism
- And so much more…
For example lets say you want to tell a company like zoho that you own a dowmain name. Zoho can say, OK if that is you domain name, then prove it by updating the domain DNS and add some data that only I(zoho) know about. If you own the domain only you can update the DNS. Here is my my secret data. So I would go into my DNS manager, and add the secret code in my DNS. Then Zoho would query the my DNS record to see if their secret is there. If it is them the assumption is I own it.
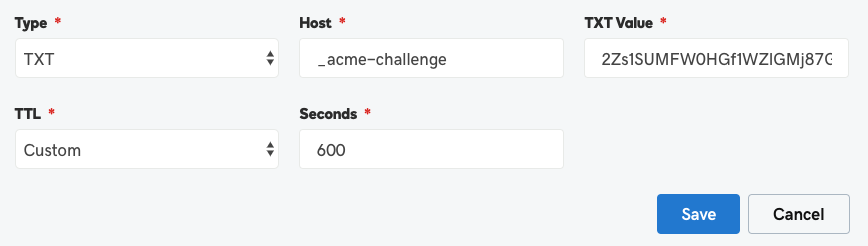
That type of task or transaction is common when doing things like buying a domain name, and then hosting your email for your domain name in a cloud service like Zoho. What they will do is ask you to create a TXT record in your DNS.
DNS Records have types. Below is how you would or Zoho in this situation would query DNS to see what txt records exists for a domain. Keep in mind everything in DNS is public to the world, so never put anything that should not be shared with the world in it.
To check a TXT record in nslookup
jaywalker@Jays-Mac-mini ~ % nslookup -type=txt techaid.me
Server: 192.168.5.1
Address: 192.168.5.1#53
Non-authoritative answer:
techaid.me text = “zoho-verification=zb92426001.zmverify.zoho.com”
techaid.me text = “v=spf1 include:zoho.com ~all”
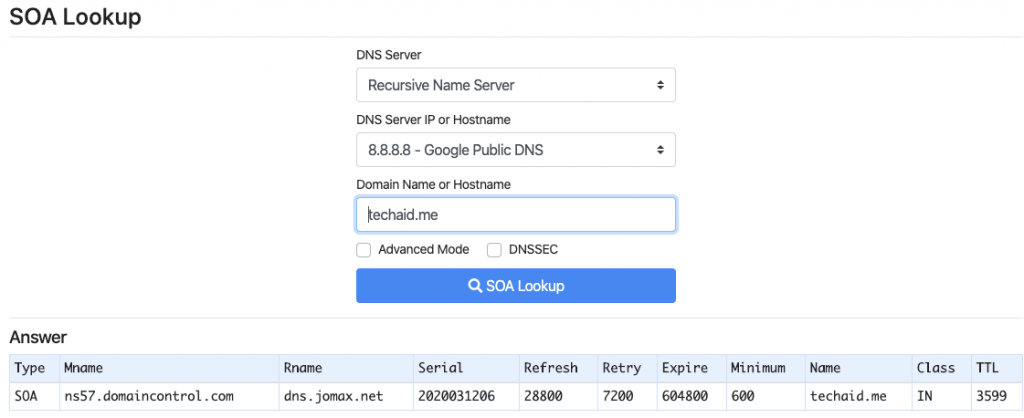
Another type that exists is what is called SOA (Start of Authority). Ever domain name has a single master DNS Record. Then that master DNS record is copied throughout the world so that where ever you are in the world, you have a DNS server close to you with information to lookup the computer IP address of a human DNS Name by service type. What is actually copied is who the SOA is, then if the DNS name is looked up one time, that info is cached. But more on that later.
Find Start of Authority DNS Server
jaywalker@Jays-Mac-mini ~ % nslookup -type=soa techaid.me
Server: 192.168.5.1
Address: 192.168.5.1#53
Non-authoritative answer:
techaid.me
origin = ns57.domaincontrol.com
mail addr = dns.jomax.net
serial = 2021092400
refresh = 28800
retry = 7200
expire = 604800
minimum = 600
Authoritative answers can be found from:
Caching and the Design of DNS
Like we said earlier, SOA’s are the master record of a DNS name. And what is copied all over the world to other DNS servers is the SOA to Domain name list to top level domain servers.
Whats a Top Level Domain?
.com or .us or .net or .org
Top is all the way to the right, everything to the right of the very last period.
So if you have a domain name like mybigchicken.com the top level domain name is .com and your domain name is mybigchicken.com. And there is a server out there that has all the SOA server to your domain name index on it.
Root Servers
Root zones are authoritative name servers that serve the DNS root zone. Most people call them “Root Servers”. Its basically a bunch of servers around the world.
https://www.iana.org/domains/root/servers
OK, so we are going to get a little in the weeds here. When I say a bunch of servers I mean hundreds. For example SCJohnson out of Racine Wisconsin in the US has some root servers. All of this information is public information. And the Governing authority IANA has an agreement with SCJohnson about how they will manager their root servers. There is a lot of work and responsibility when running a root server, take a look and explore the agreements in the link below.
https://www.icann.org/en/registry-agreements/details/afamilycompany?section=agreement
Root servers have every SOA for every top level domain name. In addition to some top level domain name A(CNAME) and AAA Records. For example, there are servers a-m(13 servers) for the .com domain name.
com. 172800 IN NS a.gtld-servers.net. com. 172800 IN NS b.gtld-servers.net. com. 172800 IN NS c.gtld-servers.net. com. 172800 IN NS d.gtld-servers.net. com. 172800 IN NS e.gtld-servers.net. com. 172800 IN NS f.gtld-servers.net. com. 172800 IN NS g.gtld-servers.net. com. 172800 IN NS h.gtld-servers.net. com. 172800 IN NS i.gtld-servers.net. com. 172800 IN NS j.gtld-servers.net. com. 172800 IN NS k.gtld-servers.net. com. 172800 IN NS l.gtld-servers.net. com. 172800 IN NS m.gtld-servers.net.
Here is how a query works. We will use the example of sherry turns on a computer, opens a web browser, and navigates to www.brandnewdomain.com
- Sherrys computer web browser will look at the computers storage memory(cache) for a existing dns lookup for www.brandnewdomain.com. Lets say Sherry never went to the web site before, sherrys computer will now look at the computers network configuration, and find out what the DNS servers are on sherrys computer. And send a query to the DNS servers. Probably a local internet service providers computer. Sherrys computer will not send that query to that area DNS Server. Lets say the computers DNS IP is 71.10.216.1 which belongs to rns01.charter.com
- The internet service providers(ISP) DNS server rns01.charter.com lets say has never looked up www.brandnewdomain.com, in that case the charter.com dns server will reference a root server to find out what DNS server in the world has www.brandnewdomain.com master DNS Record. If the charter DNS server had looked up the domain name, the ISP DNS server would have simple returned the IP address to sherry. The ISP will reference the list of Root Servers which exist on every DNS Server starting with the first one. If offling or busy, the next root server is tried. The Root server tells the ISP DNS server to try the server a.gtld-servers.net. This server will know what SOA DNS IP(Start of Authority Domain Name Server Internet Protocol Address).
- You might as, how does the ISP DNS server know what the IP of the a.gtld-servers.net is? good questions, the Root servers always have the lookup IP address of all top level domain name DNS servers.
a.gtld-servers.net. 172800 IN A 192.5.6.30
- So now the ISP DNS server reaches out to 192.5.6.30 and asks the question, What is the SOA for www.brandnewdoamin.com. And the IP 192.5.6.30 responds with ns1.namebrightdns.com. Now the ISP DNS server sends a query to ns1.namebrightdns.com and asks whats the IP of the host name www.brandnewdoamin.com which responds to the ISP DNS which is cached on the ISP DNS server ffor the amoutnof time in the expire setting of the domain name (TTL), the the ISP DNS forwards that response to Sherrys computer, which in tern also caches(remembers) the IP address lookup for www.brandnewdomain.com.
- If the domain name is tried again for Sherry or anyone else who uses the ISP DNS server, the cached record is used instead of having to back to root servers and then a SOA server.
There you have it. An system designed for redundancy and efficiency and control. Does a lot of work and provides a lot of servers, and it is free. Kinda, but not really. Cost to run all this infrastructure is spread out through tons of servers like internet connections, hosting costs and so much more.